Kaggle 离线使用YOLOv5——Global Wheat Detection
Kaggle 离线使用YOLOv5——Global Wheat Detection
Kaggle上很多比赛都要求代码在离线(offline)状态下运行的,虽然notebook的运行环境已经自带了很多深度学习和神经网络的包,但是要运行GitHub上下载的YOLOv5模型还差一些包和环境需求导致不能直接运行。而且离线状态下也不允许使用git命令克隆仓库。
那我直接上传最终submission.csv不就行了?很遗憾不行的。因为最终分数会扩大测试数据重新测试你代码运行的结果,这其实也是为什么要offline的原因,防止有人利用网络将扩大的数据集传出来以致于不公平。
我本来是想用Global Wheat Detection练习一下YOLOv5的使用,但是因为离线环境确实困扰了我几天的时间。我对Kaggle的notebook到底是怎么运作的并不清楚,而且网上鲜有这样的教程。网络上搜不到答案只有两种情况:一是这真的很难,没有人能做出来(我的问题当然不是这种情况);二是答案很简单,不值得出教程(事实确实是这样)。不过还是在此记录一下我是怎么实现的吧
Notebook环境说明
Kaggle的Notebook实际上是一个.ipynb编辑器,支持code和markdown两种语言进行编写,我们可以分段编写和运行代码。因为notebook能持续保持运行状态,可以一块一块地执行代码,且前面的执行结果和变量依然有效。
设置可以更改运行是否使用GPU,这里需要注意,要在代码运行之前就进行选择,因为更换GPU不是热加载,而是直接更换一个新的运行环境,之前运行的环境会丢失。
右边sidebar(如果没有在view里点击show sidebar)可以加载数据集。如果你是在比赛的code页面点击的new notebook,那么可以看到input自动加载了这场比赛的数据集。
可以自行添加数据到input里面,有两种方式:一是从网站已有的数据进行添加,比如其他比赛的数据集,或者是你自己其他notebook上的产出文件(Output);二是从自己电脑上传压缩包文件,上传的时候会询问是model还是dataset,其实还是第一种方式加载数据,你上传的文件会先保存到网站上,然后再加载。你上传的压缩文件会自动解压到当前环境的input目录下。
注意,所有notebook都有两个路径可以使用,一是/kaggle/input/,这个是存放所有准备使用的文件的,这个文件夹只读,不能更改;二是/kaggle/working/,这个文件夹是你代码所有产出保存文件的地址,这个文件夹没有只读的限制,可以随意更改,但是有上限20GB的要求。在运行Save&Run All(Commit)保存这个版本的Version的时候,Kaggle会自动从头到尾运行代码,而且保存这个notebook的/kaggle/working/下的所有文件。当你在新notebook里面,可以添加这个notebook的output,会保存在新notebook的/kaggle/input/的文件夹下。
建议先将所有文件复制到working文件夹下在进行其他操作,处理数据会比较方便。
实现方法
因为是边试错边完成的,所以步骤有些冗余。
我一共创建了三个notebook和一个dataset。notebook分别是YOLOv5&Dependences,WheatDetectOffineTrain和WheatDetectOfflineDetect。一个数据集是ArialTTF,其实就是Arial字体文件。
这里强调一下,模型的训练和检测建议分成两个notebook来写,因为提交之后会运行你的代码,如果重新训练的话会花费大量的时间才能得到分数。
ArialTTF
先说一下这个数据集吧,这是在用YOLOv5训练的时候报错发现的,它说没有Arial字体文件。因为YOLOv5训练结束后会展示一些图片,上面会画框和标注标签,需要字体文件。Arial应该是最基本的英文字体文件了,然而Kaggle环境里并没有,所以需要在input加上这个字体文件,下面会提到怎么处理这个字体文件。
创建方法很简单,在notebook编辑页面点击上传input,选择dataset,上传在网上下载好的字体文件即可。
YOLOv5&Dependences
这个notebook可以连接网络。其实只有最后提交的notebook offline就行。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。
WTF,WTF,WTF。。。。。。
所以我为什么要写三个notebook,我为什么要在train的时候也离线了。。。
我真的是写到这里的时候才意识到这个问题。
因为当前这个YOLOv5&Dependences notebook主要解决的是离线notebook不能使用git,pip命令进行在线操作的问题。我想的是在这里下载好YOLOv5和依赖包之后,在WheatDetectOffineTrain里面作为input进行加载就可以离线使用YOLOv5了。
实际上WheatDetectOffineTrain完全可以联网下载和安装依赖,所以这个notebook完全没有存在的必要。
我终于明白discussion里面有人说的你需要创建两个notebook,一个用来训练,一个用来检测是什么意思了。并不是需要,而是“只”需要两个。
不过还是记录一下这个notebook的代码吧:
1 | !git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 |
因为预训练文件是在线加载的,所以也得提前下载。。。
WheatDetectOffineTrain
好,接下来记录一下这个“离线”训练的notebook。
首先要先添加input,将上面两个加载进来。
然后安装依赖:1
!pip install --no-index --find-links=/kaggle/input/yolov5-dependences/yolov5/dependences -r /kaggle/input/yolov5-dependences/yolov5/requirements.txt
这里运行完后会看见报错:1
2
3ERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts.
torchaudio 2.6.0+cu124 requires torch==2.6.0, but you have torch 2.7.1 which is incompatible.
fastai 2.7.19 requires torch<2.7,>=1.10, but you have torch 2.7.1 which is incompatible.
好像是因为本地torch版本太高了,不过不用理会,代码能正常运行。
创建数据集文件夹1
2import os
os.makedirs('/kaggle/working/wheat', exist_ok=True)
将标签转换成YOLO格式:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43import pandas as pd
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
from PIL import Image
# set path
csv_path = r'/kaggle/input/global-wheat-detection/train.csv'
image_dir = r'/kaggle/input/global-wheat-detection/train'
label_output_dir = r'/kaggle/working/wheat/labels'
os.makedirs(label_output_dir,exist_ok=True)
df = pd.read_csv(csv_path)
# 解析 bbox 字符串为 float 类型的 [x, y, w, h]
df[['x', 'y', 'w', 'h']] = df['bbox'].apply(lambda x: eval(x)).apply(pd.Series)
def convert_bbox_to_yolo(size,box):
"""
size: (width,height)
box: (x_min, y_min, width, height)
return: normalized (x_center, y_center, width, height)
"""
dw, dh = 1. / size[0], 1. / size[1]
x_center = (box[0] + box[2] / 2.0) * dw
y_center = (box[1] + box[3] / 2.0) * dh
w = box[2] * dw
h = box[3] * dh
return x_center, y_center, w, h
for image_id, group in tqdm(df.groupby('image_id'), desc="Generating labels"):
image_path = os.path.join(image_dir,image_id + '.jpg')
label_path = os.path.join(label_output_dir, image_id + '.txt')
if not os.path.exists(image_path):
continue
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
img_w, img_h = img.size
with open(label_path,'w') as f:
for _, row in group.iterrows():
x_center, y_center, w, h = convert_bbox_to_yolo((img_w, img_h), (row['x'], row['y'], row['w'], row['h']))
f.write(f"0 {x_center:.6f} {y_center:.6f} {w:.6f} {h:.6f}\n")
输出:Generating labels: 100%|██████████| 3373/3373 [00:23<00:00, 144.72it/s]
整理图像文件夹,符合YOLO要求,划分训练集验证集。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50import os
import shutil
import random
from pathlib import Path
image_dir = Path(r'/kaggle/input/global-wheat-detection/train')
label_dir = Path(r'/kaggle/working/wheat/labels')
output_base = Path(r'/kaggle/working/wheat/yolo')
os.makedirs(output_base,exist_ok=True)
train_ratio = 0.8
output_images_train = output_base / 'images/train'
output_images_val = output_base / 'images/val'
output_labels_train = output_base / 'labels/train'
output_labels_val = output_base / 'labels/val'
# 创建目标文件夹
for path in [output_images_train, output_images_val, output_labels_train, output_labels_val]:
os.makedirs(path, exist_ok=True)
image_files = list(image_dir.glob('*.jpg'))
# stem is to remove .jpg
image_ids = [img.stem for img in image_files]
random.seed(42)
random.shuffle(image_ids)
split_index = int(len(image_ids) * train_ratio)
train_ids = image_ids[:split_index]
val_ids = image_ids[split_index:]
def copy_files(image_ids, image_dst, label_dst):
for image_id in image_ids:
src_img = image_dir / f"{image_id}.jpg"
dst_img = image_dst / f"{image_id}.jpg"
shutil.copy2(src_img,dst_img)
src_label = label_dir / f"{image_id}.txt"
dst_label = label_dst / f"{image_id}.txt"
if src_label.exists():
shutil.copy2(src_label, dst_label)
else:
dst_label.write_text('')
copy_files(train_ids, output_images_train,output_labels_train)
copy_files(val_ids, output_images_val,output_labels_val)
print(f"✅ 划分完成:{len(train_ids)} 张用于训练,{len(val_ids)} 张用于验证。")
输出:✅ 划分完成:2737 张用于训练,685 张用于验证。
注意:没有框的图片也需要一个对应的空txt文件
编写yaml文件:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11yaml_content = """
path: /kaggle/working/wheat/yolo
train: images/train
val: images/val
nc: 1
names: ['wheat']
"""
with open("wheat.yaml", "w") as f:
f.write(yaml_content)
将YOLOv5拷贝到working文件夹:
1 | !cp -r /kaggle/input/yolov5-dependences/yolov5 /kaggle/working/yolov5 |
因为YOLOv5在运行的时候wandb会联网进行git检查,然而当前是offline的,会造成无法运行的情况。这里使用了chatgpt教我的“猴子戏法”,将执行检查的函数无效化:
1 | import types |
安装字体文件,我们只需要将字体文件移动到yolo会寻找字体的地方即可:
1 | !mkdir -p /root/.config/Ultralytics/ |
执行训练命令,这里先进入到YOLO文件夹下,简化命令:1
2cd /kaggle/working/yolov5/
!python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 50 --data /kaggle/working/wheat.yaml --weights weights/yolov5s.pt --name wheat_yolov5
到此就可以了,执行Save & Run All(commit)等待训练完成后就可以进行检测了。我并没有进行图片增强,增加数据集的操作而直接训练的,所以最后检测结果会有一点低。
WheatDetectOfflineDetect
提前加载字体文件,YOLOv5&Dependences和WheatDetectOffineTrain的output。
突然意识到YOLOv5&Dependences也还是有一点存在的必要的,检测文件也需要安装环境,虽然说在训练文件里也可以下载。
安装依赖:1
!pip install --no-index --find-links=/kaggle/input/yolov5-dependences/yolov5/dependences -r /kaggle/input/yolov5-dependences/yolov5/requirements.txt
拷贝训练后的YOLOv5文件夹:1
!cp -r /kaggle/input/wheatdetectoffinetrain/yolov5 /kaggle/working/yolov5
这时yolov5项目文件夹里是有训练后的runs文件夹的。
安装字体:1
2!mkdir -p /root/.config/Ultralytics/
!cp /kaggle/input/arialttf/Arial.ttf /root/.config/Ultralytics/Arial.ttf
转换工作目录:1
cd /kaggle/working/yolov5/
检测命令:1
!python detect.py --weights runs/train/wheat_yolov5/weights/best.pt --source /kaggle/input/global-wheat-detection/test --img 640 --conf 0.25 --save-txt --save-conf --project runs/predict --name wheat_test
这里说明一下,--conf是保留置信度,--save-txt是保存为txt文件。
转换yolo输出并生成submission.csv文件:
1 | import os |
最终分数如下: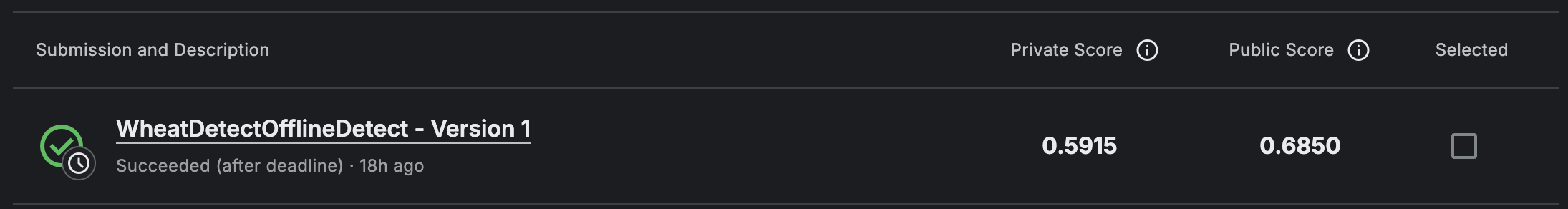
分数和榜单上还差很多。经过几天的搜索关于目标检测竞赛的信息和查看别人的解决方案,我认为直接使用YOLO可能是一个非常坏的选择。
PS:封面图来源:百鬼あやめ😈ホロライブ2期生







